Getting Environmental Sensor Information (Temp, Humidity) with Raspberry Pi 3
PROJECT INFO
Difficulty: Advanced
Estimated time: 2 hours
License:GPL3+
THINGS USED IN THE PROJECT
Hardware components:
- NodeMCU ESP8266 Breakout Board x1
- DHT11 Temperature & Humidity Sensor x1
- LED (generic) x1
- Resistor 221 ohm
- Android Phone x1
- Breadboard x1
Software apps and online services:
- Arduino IDE
- IoTIgnite Service Registration
- IoTIgnite Agent APP
- IoTIgnite Service APP
Hand tools and fabrication machines:
- Soldering iron (generic)
STORY
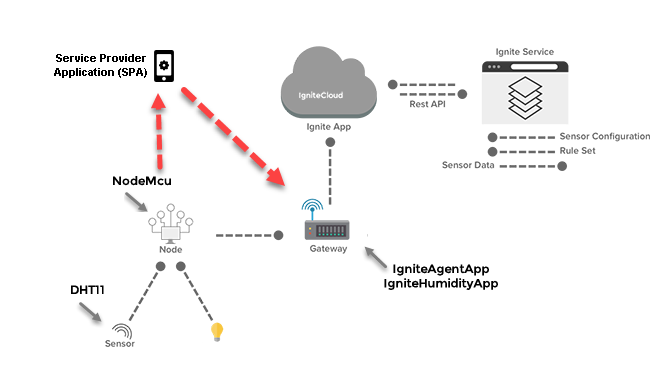
Basically, the Project will transfer data with DHT11 over wireless through NodeMCU. This transfer will be done by using an Raspberry PI3 device as a gateway, and light a led by a rule we set.
- NodeMCU will be WiFi Accsess Point; start transmitting your IP and port number to network.
- Save device to system on AP mode, and establish wireless connection.
- Once the client connection is set; read the frequency of temperature and humidity transmission, and start transmitting the data to client in this frequency.
- Re-connect to network if connection is lost, end client connection and wait for the re-connection.
- Execute when LED event happened.
1 Getting Ready forRaspberry PI3 As IoT Gateway
- Download and install IoT-Ignite Agent App from this link,
- Register and login free developer account at https://devzone.iot-ignite.com/dpanel/login.php?page=development ,
- Create a service and choose a service name and click next,
- Setup and install Raspberry Pi 3 using a micro SD card that contains the latest IoTAgent
2 Prepare NodeMCU for Gateway Registration
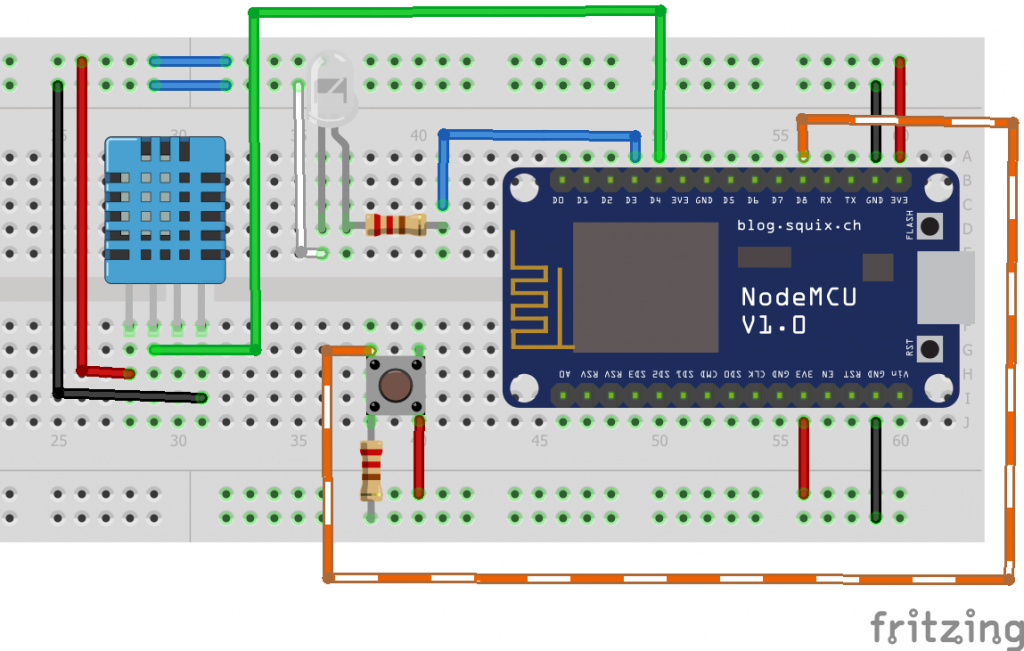
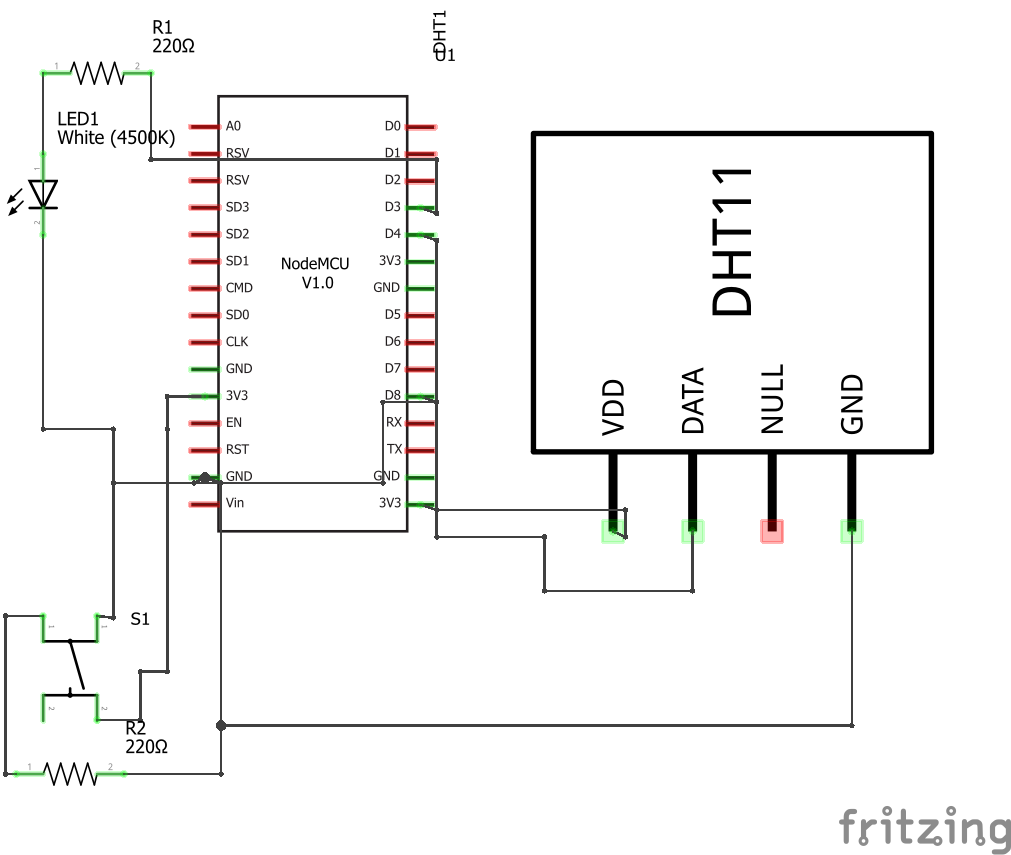
Step 1: Components Connect the DHT11, Resistor and the LED
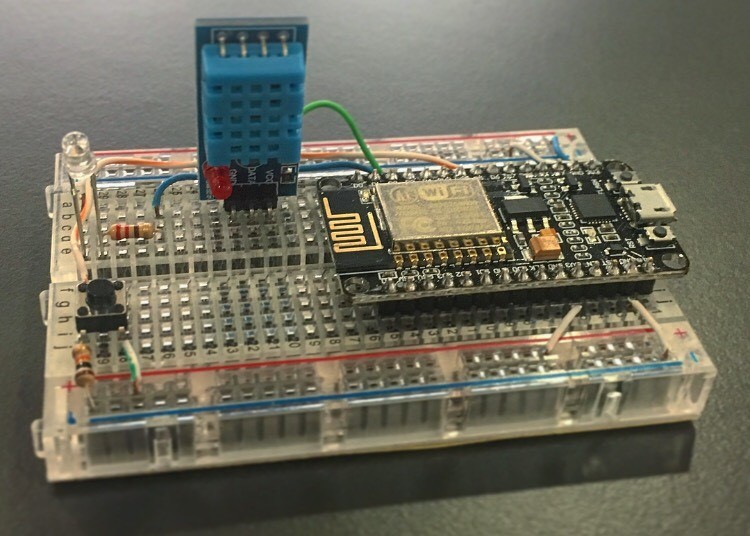
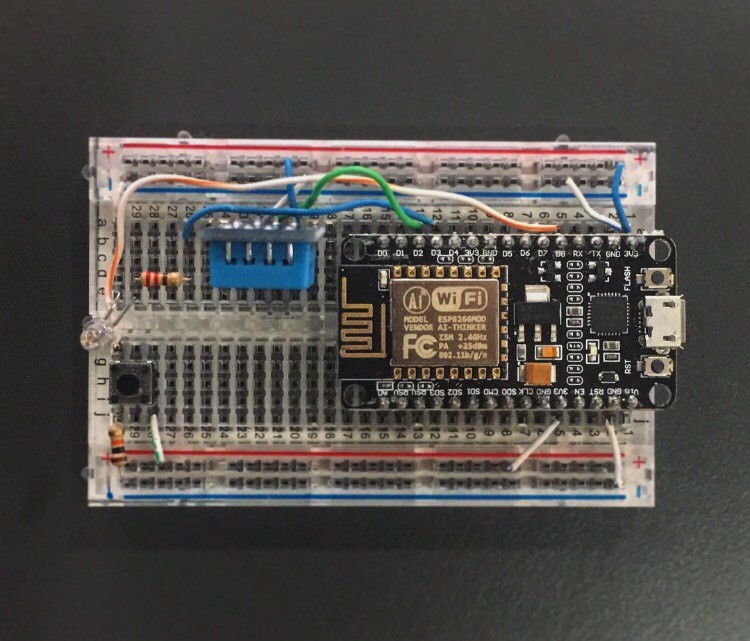
Connect the pins as shown below for device’s physical connection (this connection is configured for the provided sample codes):
The set is physically ready. Now follow the steps to make the set ready for computer installation of the necessary software.
Step 2: Getting Ready for NodeMCU
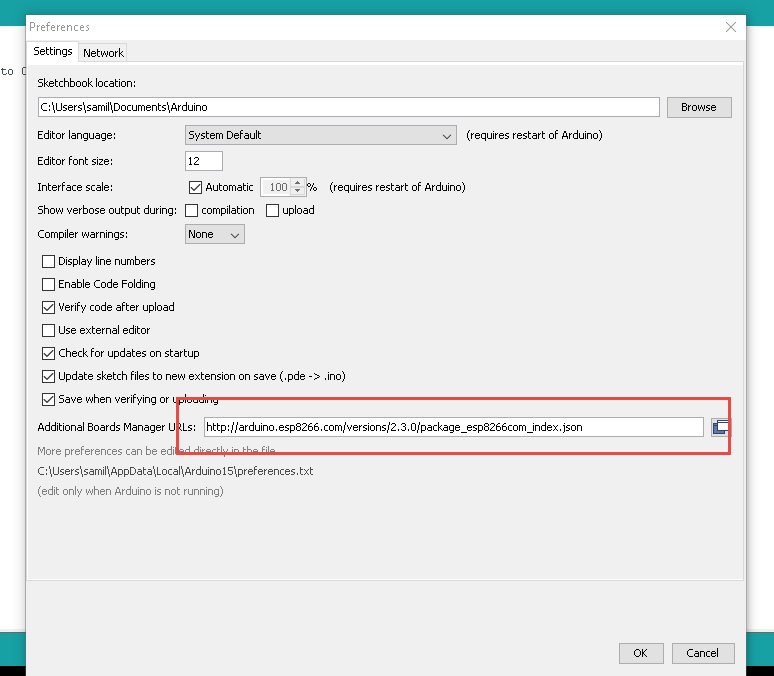
Go to File/Preferences and add additional esp8266 library from the link below to introduce Arduino IDE with NodeMCU to make it programmable.
http://arduino.esp8266.com/versions/2.3.0/package_esp8266com_index.json
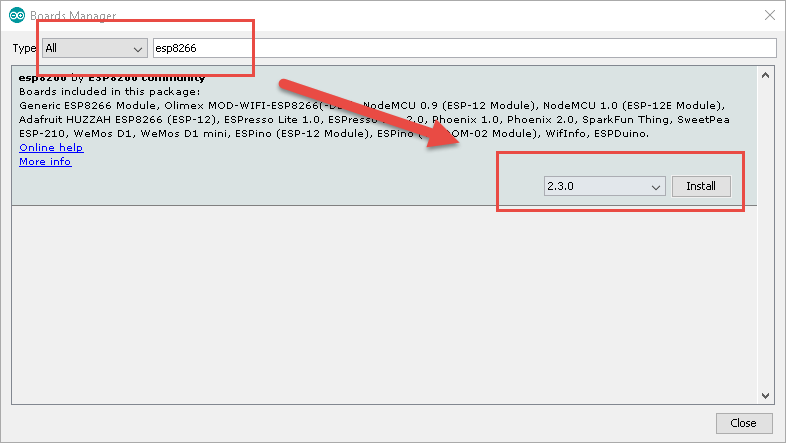
Go to Tool menu and enter esp8266 on board manager screen and click install to finish installation.
Step 3: Installing File System and Libraries
Getting ready for installing NodeMCU file system. Download filesystem uploader plugin here for this https://github.com/esp8266/arduino-esp8266fs-plugin/releases/tag/0.2.0, and extract under Arduino IDE as C:\Program Files (x86)\Arduino\tools\ESP8266FS\tool
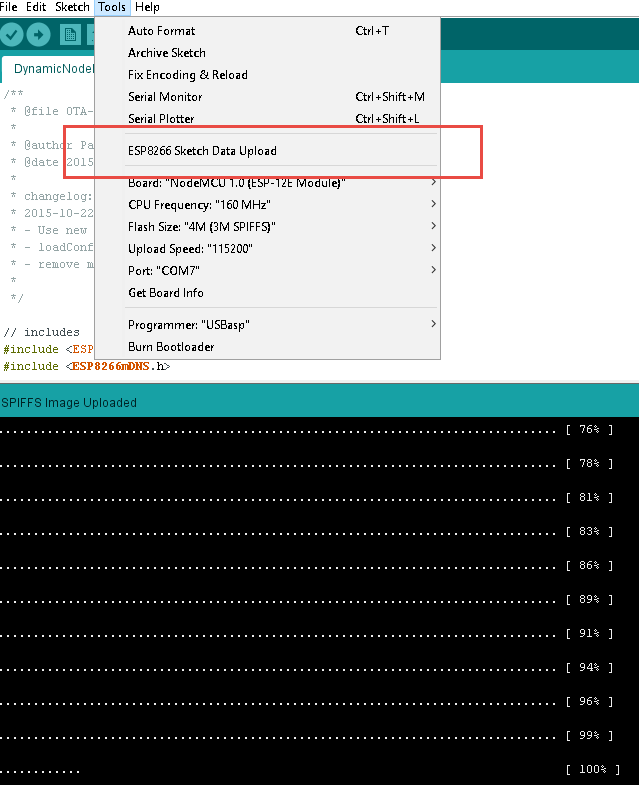
Re-start Arduino IDE and make it ready by data upload under Tools menu.
Here we will install the libraries to be used for the application.
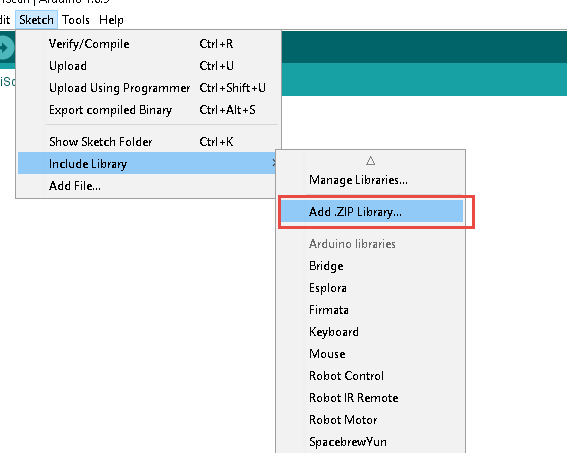
For timer library; download from https://github.com/JChristensen/Timer, and add the file to IDE by “sketch include library, add zip library”.
Install other general libraries such as ESP8266WiFi, ESP8266mDNS, WiFiUdp, FS ve DHT as well (Sketch > Include Library > Manage Library).
Add the program code to Arduino and make sure about the computer port we connect the NodeMCU.
Step 4: Generate, Compile, and Upload Code
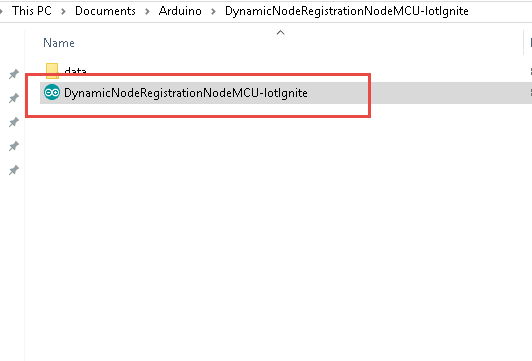
Copy the library in files within the Github library to extract in Ardunio IDE, i.e: C:\Users\{name}\Documents\Arduino\DynamicNodeRegistrationNodeMCU-IotIgnite
Make sure the data files are under C:\Users\{name}\Documents\Arduino\DynamicNodeRegistrationNodeMCU-IotIgnite\data , and double click file to open.
Now the set is ready with NodeMCU after uploading is done.
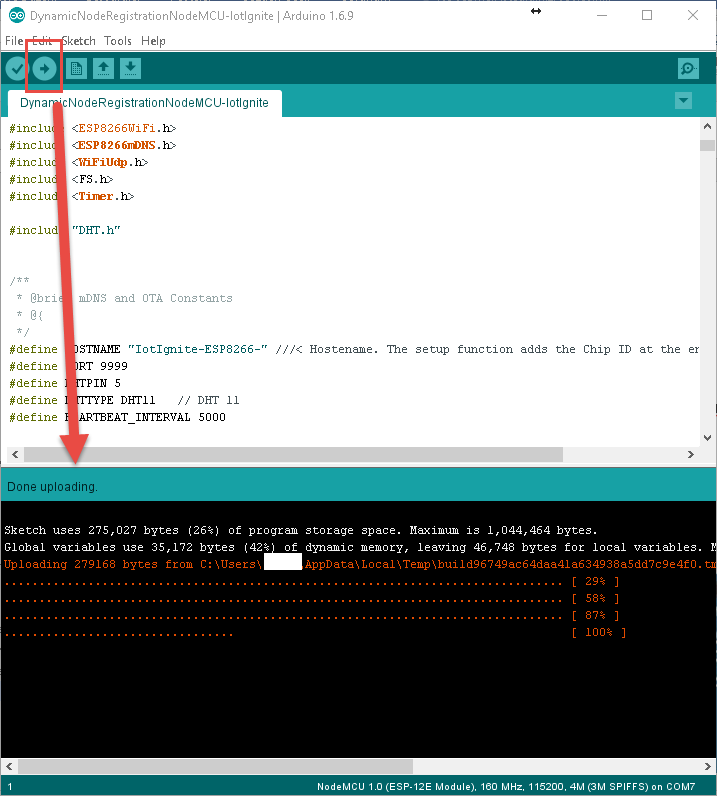
NodeMCU must be acces point when your upload complete. Now we can register NodeMCU to Gateway with our open source sample application as called Service Privoder Application.
3 Service Provider Application
Service provider application(SPA) is a template application (open source) for developers mass deployment process. You can use one distribution for all of customer.
- Install Service Provider Application: https://download.iot-ignite.com/ServicePlatformApp/
- Login with your devzone credentials on your service provide application.
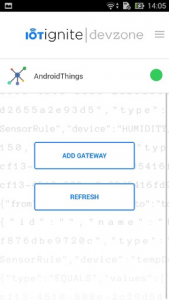
Step 1: Gateway Registration
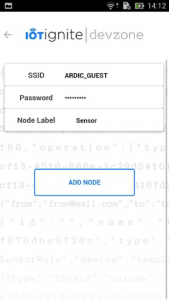
- Click add gateway and type your wireless information for connecting,
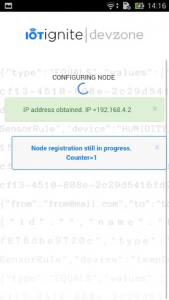
- Wait a minute for setup process.
Step 2: Register NodeMCU for Gateway
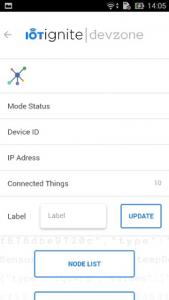
- Go home page, list your Gateways and click Thing List and Add Node Manually button.
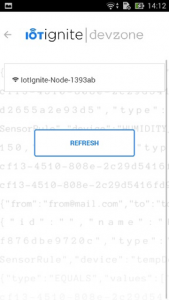
- Type your wireless information for connecting to NodeMCU.
SPA connect your NodeMCU, provides wireless and gateway information to NodeMCU. Install the user application that will transmit the data received from DHT 11 (NodeMCU) sensor to IoT-Ignite platform.

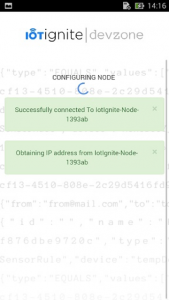
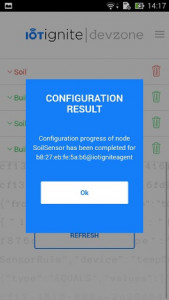
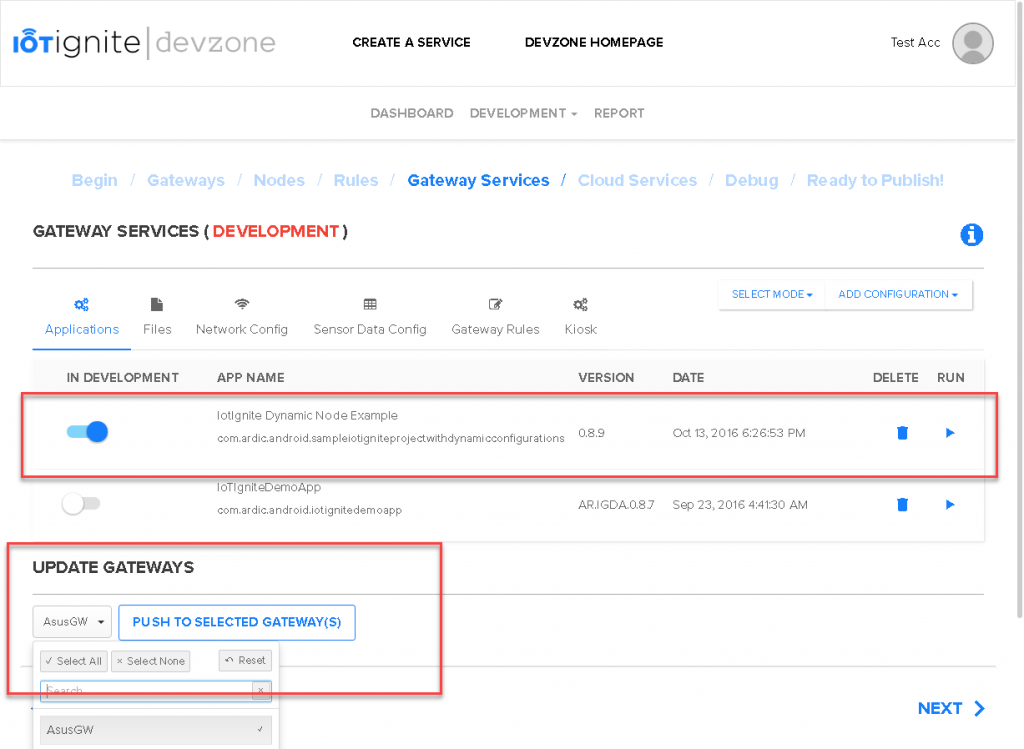
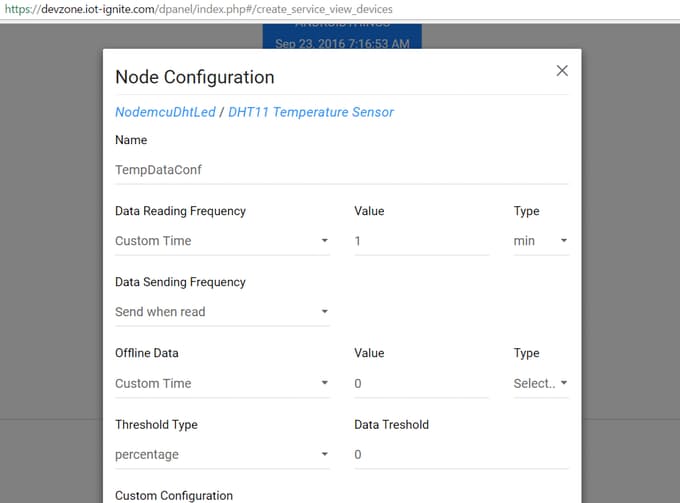
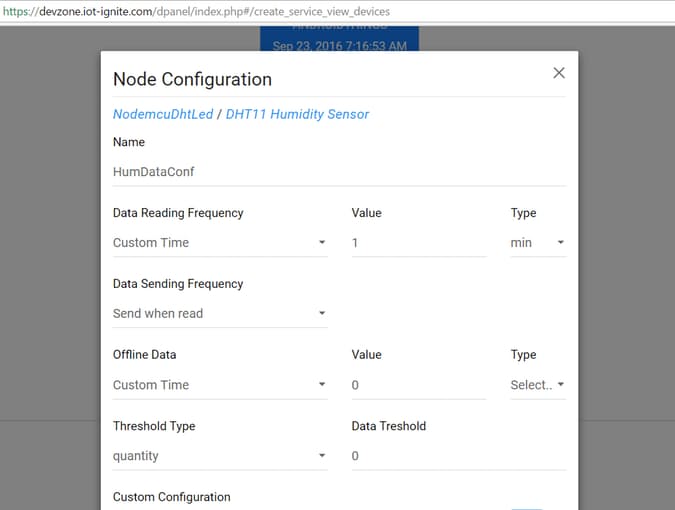
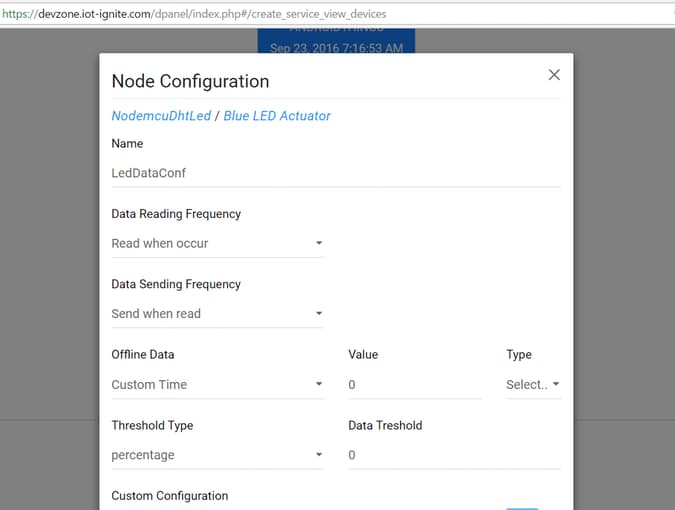
Step 3: Devzone Data Configuration – Devzone Rule
When your NodeMCU get registered, it time to configure for data configuration. Login your Devzone panel; https://devzone.iot-ignite.com
Click Developments menu item then select Nodes item Data configuration provides options for NodeMCU;
- Data Reading Frequency
- Data Sending Frequency
- Threshold Type
- Offline Data
- Custom Configuration
Our example data reading and sending frequency type must be custom and min value is 1 min.
Set the the values. After the configuration, must be pushed to device after change.
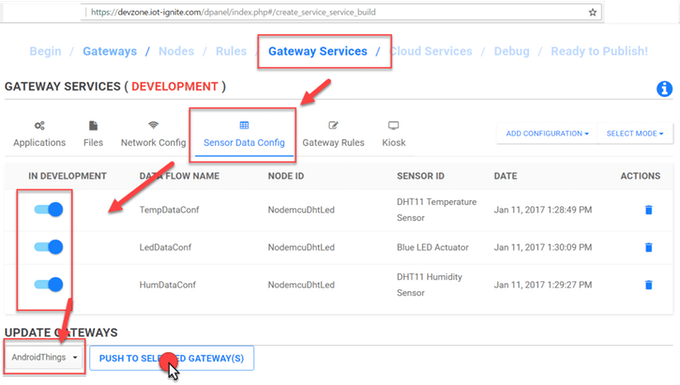
Finally IoT-Ignite will collecting data from sensors in the selected time range.
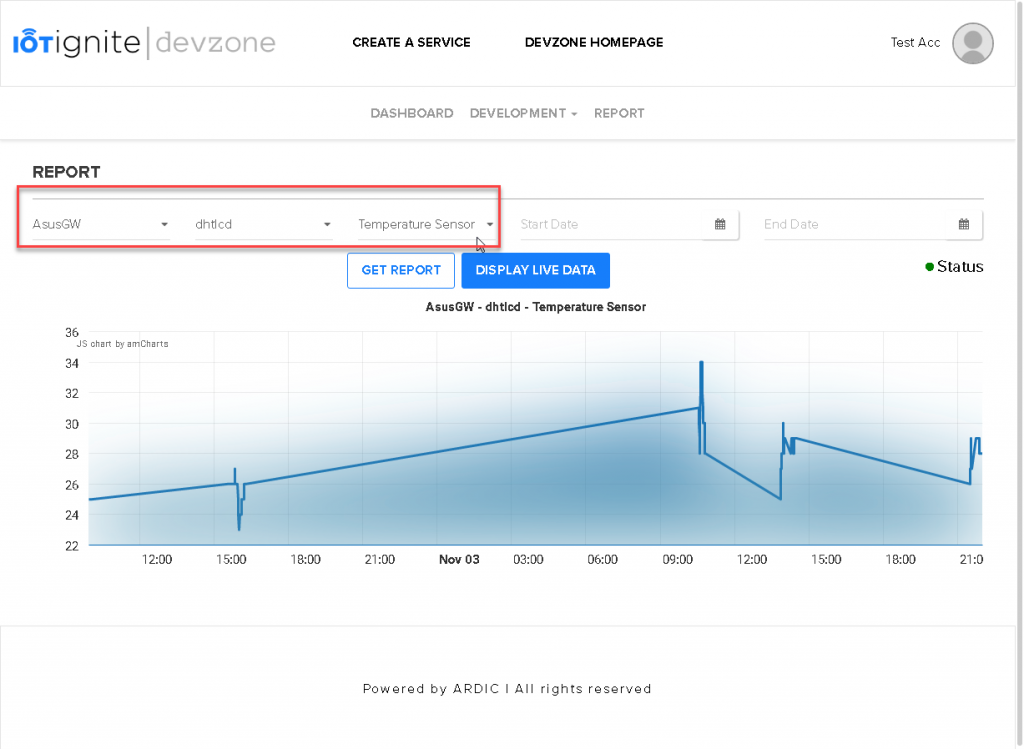
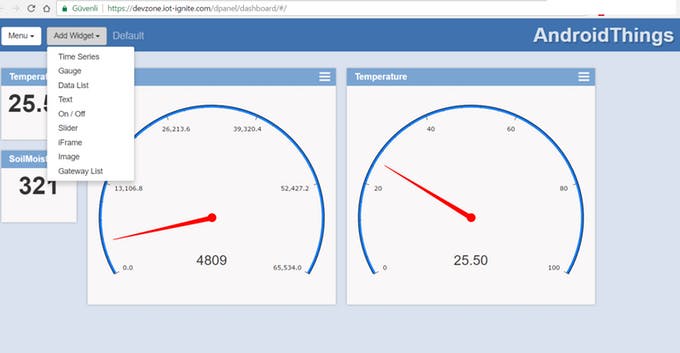
Step 4 Play Time: Devzone Dashboard – Devzone Report
Devzone have two visual reporting tool. You can use report tab and IoT Dashboard page. Report tab is simple data listing and visualization tool.
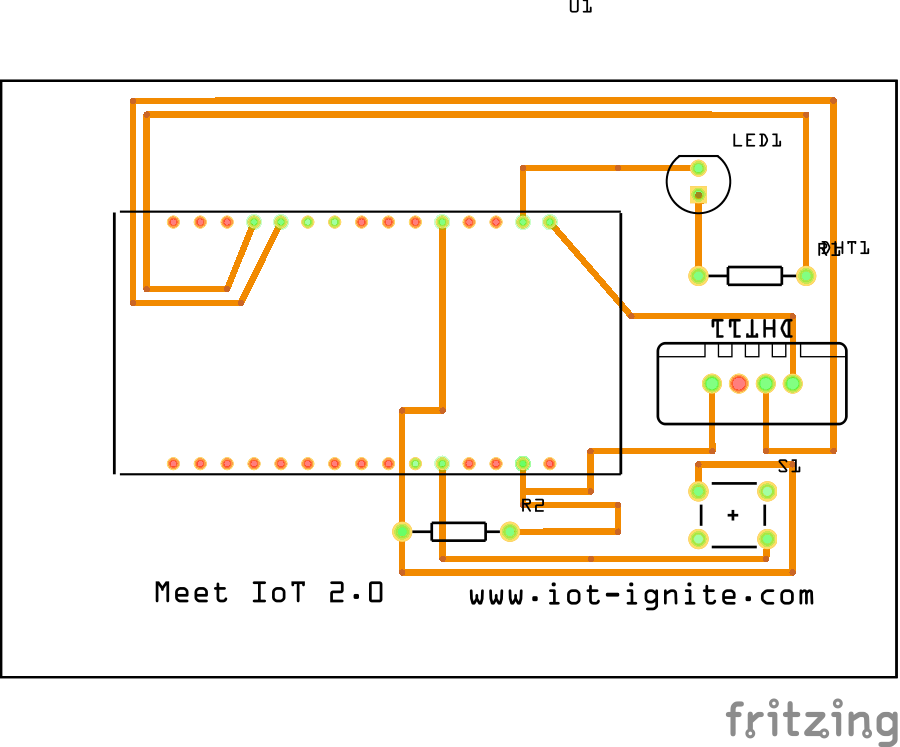
SCHEMATICS
Circuit
NodeMCU DHT11 and Led Circuit
CODE
Github
You can access the project files on git hub. Click here to access; ino files to code on NodeMCU as well as all application source code for Android.
Source Code: https://github.com/IoT-Ignite/arduino-sketch-dynamic-node-example
Arduino ESP8266 filesystem uploader plugin: https://github.com/esp8266/arduino-esp8266fs-plugin








Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!